Waterfall vs. Agile: Which Methodology to Choose for Your Redmine Projects?

Sometimes I hear shouts like "Gantt is dead," "you have to drive it the agile way," or even "project management is dead." Although many of them are just an example of marketing rubbish, I often encounter project portfolio managers, scrum masters, and other project management professionals who want to seriously argue about Agile vs. Waterfall (Gantt) techniques. This post is a brief introduction to the topic.
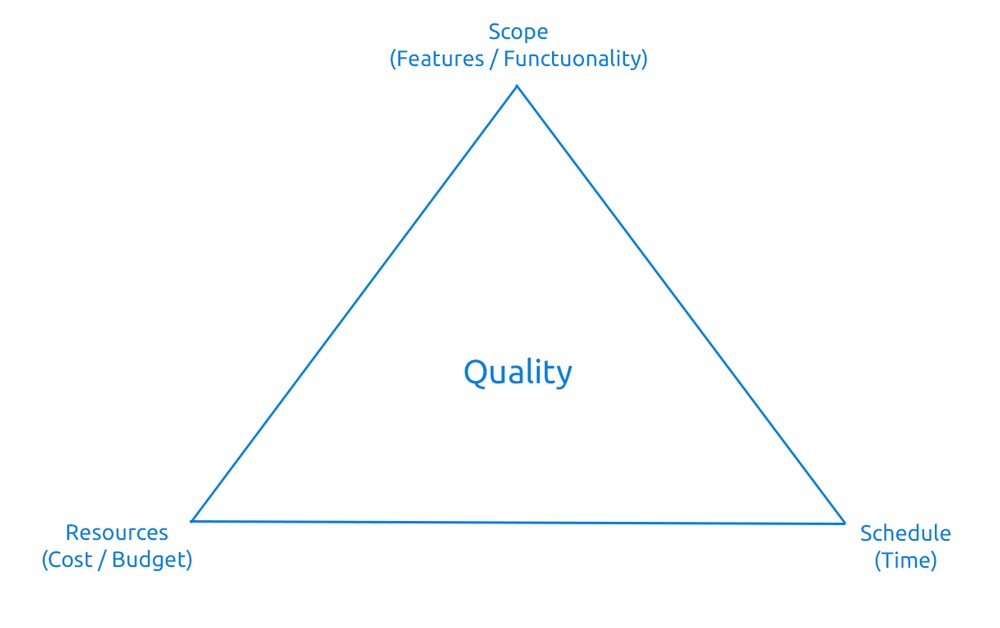
The iron triangle of project management
The iron triangle is actually a very simple representation of the key elements needed for successful project planning. Scope, time, and cost/resources. Resources are the only and/or critical elements of the price in many industries. People are the most valuable asset that cannot simply be increased, reduced, or multiplied. Similarly, machine resources have a certain production capacity and cannot be changed by a simple click.
Easy Redmine - The iron triangle #1
But how does the iron triangle fit into the overall picture? Very conveniently. It offers us a simple but effective answer when we should use the planning of the Waterwall methodology and, on the contrary, when to choose an agile approach.
Redmine Waterfall project management
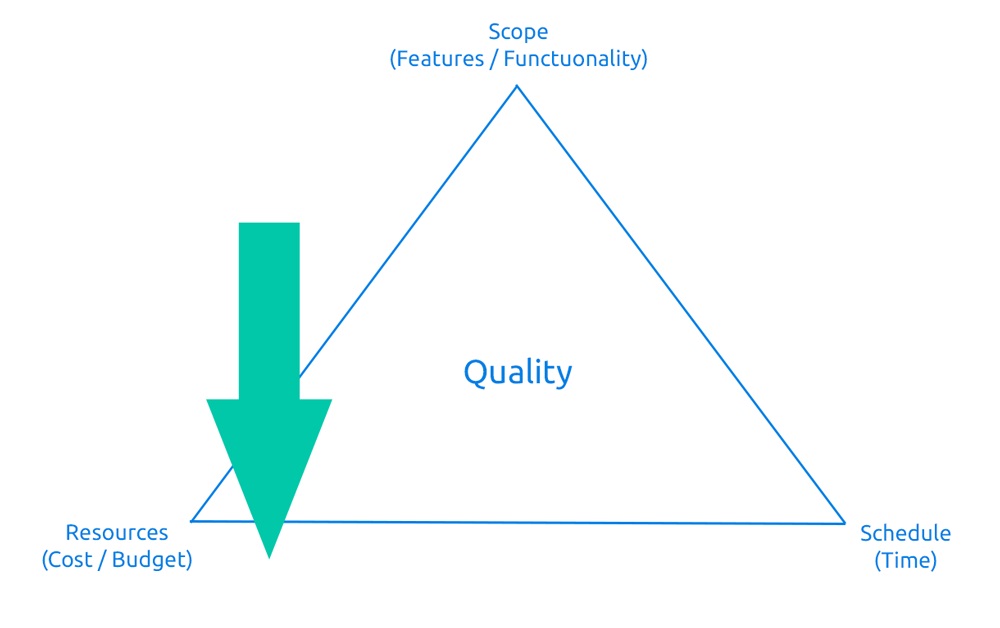
The Waterfall methodology is best suited to a project whose scope is precisely defined and is a key element of the project, such as real estate construction, conference planning, or Easy Redmine software implementation.
Technique: The scope of the project is defined (fixed). In our example, this means that I cannot change the number of windows in my real estate, I cannot change the place or subject of a conference, etc. The project time is a limiting factor either absolutely (e.g. conferencing) or almost absolutely (e.g. software implementation). With a tightly defined scope, the main task of a project manager or portfolio manager is to schedule all types of resources on the timeline across parallel running projects and take into account the required sequence of actions (tasks) in individual projects.
Consider, for example, the construction of a house: workers responsible for cement delivery have to complete their work in a timely manner because delays caused by a lack of cement resources can prevent bricklayers from completing their own tasks. Once the concrete is firm enough, they can already be found on another site.
Easy Redmine - The iron triangle #2
Redmine Agile project management
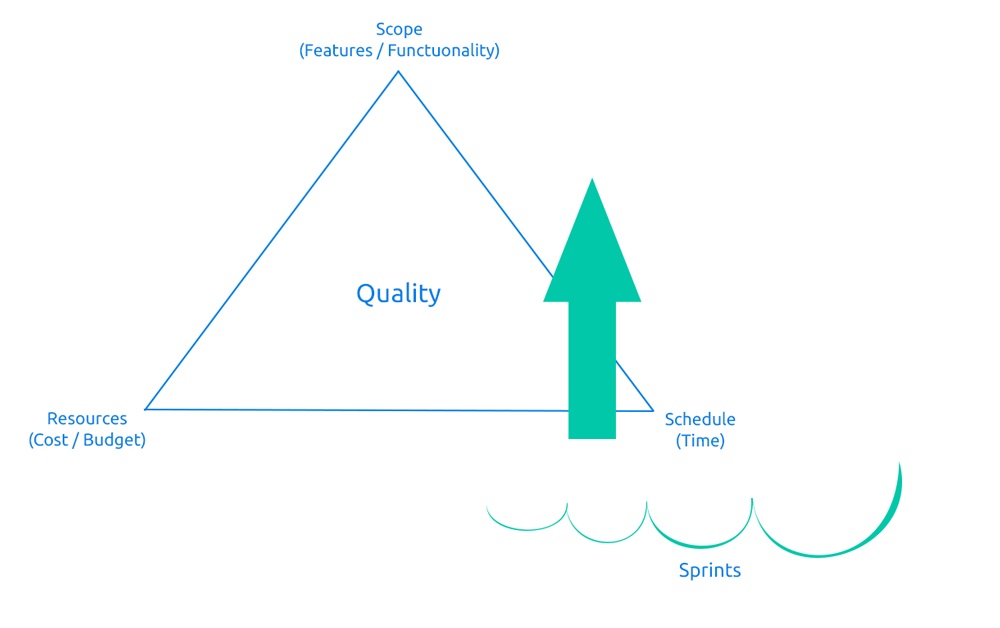
An agile approach is useful for projects where time is firmly defined, resources are a determining factor and the scope is subject to planning (prioritization). A good example could be software development (sprints), publication activity (magazine/newspaper release date), or marketing content (campaign).
Technique: scrum masters or planners in similar roles prioritize tasks for the next sprint. Usually, the scrum master has different backlogs and scrum boards for different types of resources, such as developers looking to fix bugs and handle requests for new features and, on the other side, journalists in political or sports media.
Easy Redmine - The iron triangle #3
What does it mean?
Obviously, the whole issue of project management is still turning around the iron triangle. Operational planning only focuses more on different parts of the same thing. So what can we draw from it?
- Virtually in each organization, we would find types of projects where it is necessary to use both project management techniques for creating efficient working processes. One methodology is not better than the other, it just addresses different challenges.
- Quality scheduling of resources associated with the timeline is essential for each Waterfall project, especially for project portfolio planning. The same is true for Easy Redmine projects.
- Managing agile projects: Managing priorities is usually done through various tools. Often, there is a problem with accurate resource allocation for a specific backlog. So, in this respect, I strongly recommend that you map and allocate your resources consistently. For example, a software developer can be used with multiple backlogs at the same time (e.g. bug fixes vs. function requests in the same language). Without defining quantitative resource allocation to backlogs, however, you will not be able to schedule priority deliverables, and the scrum master will have to continually resolve discrepancies between these priorities. Another unpleasant consequence will be the delayed release of new key product features such as bug fixes or feature requirements, which exploit strategic development resources.
Combination of both management methodologies
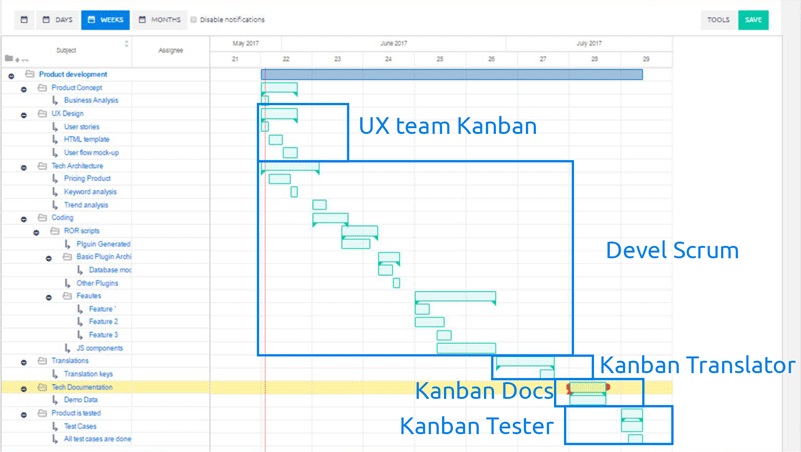
As you can see in the picture below, we have a basic Waterfall project that includes some software development plan that shows sequences and dependencies. However, teams involved in this project (salesmen, technical writers) can manage their own deliveries in their department not only as shown in this example but also in an agile way.
Easy Redmine Gantt - Waterfall project example
The ultimate Redmine upgrade? Easy.
Get all powerful tools for perfect project planning, management, and control in one software.